管道是一种进程间通信的方式,也就是 | 符号的含义
图片来自于xmind导出的svg格式,右键打开图片,查看大图。。。
要讲的东西不多,直接看代码
父子进程通信例子
示例程序
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
/*
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... // arg );
*/
void handler(int signum)
{
if (signum == SIGPIPE)
{
printf("rcv sig %d \n",signum);
exit(0);
}
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
int pipefd[2];
signal(SIGPIPE, handler);
/*
pipefd[0] 用于读
pipefd[1] 用于写
*/
ret = pipe(pipefd);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("pipe err");
exit(0);
}
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == -1)
{
perror("fork err");
exit(0);
}
if (pid == 0)
{
close(pipefd[0]);
sleep(2);
write(pipefd[1], "childssssssssssss", 10);
sleep(2);
write(pipefd[1], "childssssssssssss", 10);
printf("child quit...\n");
close(pipefd[1]);
exit(0);
}
unsigned char buf[1024];
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
close(pipefd[1]);
/*
fcntl 更改管道描述符属性为非阻塞/阻塞
*/
int flag;
flag = fcntl(pipefd[0], F_SETFL);
//flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
flag &= ~O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(pipefd[0], F_SETFL, flag);
ret = read(pipefd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));
if (ret == -1)
{
perror("read err");
}
if (ret == 0)
{
perror("read err");
}
buf[ret] = '\0';
printf("rcv : %s \n",buf);
close(pipefd[0]);
wait(NULL);
printf("parent quit...\n");
exit(0);
}- 子进程关闭读,父进程关闭写,只能有子进程想父进程写数据
- 子进程向写两次数据
- 父进程读到第一次的数据之后关闭管道的读端,此时子进程再次写管道会接收到SIGPIPE信号,该信号默认动作是退出进程,这里注册了一个新的信号处理函数
- 父进程等待子进程退出,父进程退出
实现ls | wc -w
该命令是统计当前目录下文件和目录的单词数
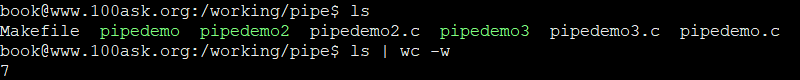
/*
实现 ls | wc -w
*/
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
int main()
{
int ret;
int pipefd[2];
/* pipefd[0] 用于读 pipefd[1] 用于写 */
ret = pipe(pipefd);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("pipe err");
exit(0);
}
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
/* 子进程执行ls 写管道 */
if (pid == 0)
{
close(pipefd[0]);
/* 复制管道的输出到标准输出 */
dup2(pipefd[1],STDOUT_FILENO);
close(pipefd[1]);
execlp("ls", "ls", NULL);
exit(0);
}
/* 父进程执行wc -c 读管道 */
else if (pid > 0)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
/* 复制管道的读到标准输入 */
dup2(pipefd[0],STDIN_FILENO);
close(pipefd[1]);
execlp("wc", "wc", "-w", NULL);
}
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}- 子进程复制管道的输出替换原来的标准输出,并拉起ls程序
- 父进程复制管道的输入替换原来的标准输入,并拉起wc -w程序
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!
